
Home, Auto Repair Library, Auto Parts, Accessories, Tools, Manuals & Books, Car BLOG, Links, Index



Ceramic brake pads are popular with many motorists today because they restore like-new brake performance, are quiet, long lasting, low dusting and provide safe sure stops. They handle heat much better than most nonasbestos organic (NAO) friction materials, and are quieter and kinder to rotors than most semi-metallic friction materials.
Ceramic brake pads first appeared in the early 90's. Some vehicle manufacturers began using ceramic-based disc brake pads in place of conventional semi-metallic pads to address customer complaints about brake noise, dust and wear. Many of these ceramic pads were supplied by Akebono. Following the OEM lead, Bosch, Raybestos, Wagner and other aftermarket brake suppliers introduced their own ceramic-based friction materials. The aftermarket ceramic pads are designed to replace OEM ceramic disc brake pads and to upgrade brake performance on vehicles that were not originally equipped with ceramic-based pads.
One of the main differences between ceramic-enhanced friction materials and semi-metallic brake linings is that ceramic pads contain no steel wool or fibers. Steel provides strength and conducts heat away from rotors, but it also makes pads noisy. Steel also acts like an abrasive and causes rotor wear. Substituting ceramic materials and copper fibers for steel allows ceramic pads to handle the high brake temperatures with less heat fade, to recovery quickly, to experience less wear on both the pads and rotors, and to virtually eliminate noise. Ceramic fibers also don't "ring" like steel fibers, so there's almost no brake noise. Annoying brake squeal is eliminated because the ceramic-enhanced compound dampens noise and moves vibrations to a frequency beyond our range of hearing.
The ceramic fibers in a ceramic-based friction material provides stable and predictable friction characteristics. The coefficient of friction with ceramic brake pads does not drop off as quickly as semi-metallics, nor does it fade as quickly as nonasbestos organic compounds as the brakes heat up. This is called "Mu Variability." The more stable the friction characteristics are, the more consistent the brake pedal feels whether the brakes are hot or cold.
Recently, some friction suppliers have reformulated their ceramic brake pads to reduce the amount of copper in the friction material. Many ceramic friction compounds have used 10 to 20 percent copper. Copper is a good conductor of heat so it functions as a friction modifier to improve cooling and fade resistance. Copper also helps reduce noise and extend the life of the pads.
Copper is going away, however, as brake manufacturers develop new low-copper and copper-free friction materials to comply with California regulations that require reducing copper content to under 5 percent by 2021. Many of the new low-copper or copper-free friction materials that have been recently introduced actually perform better than the previous generation of friction materials, with better wear, fade and noise characteristics.

Low copper or no copper brake pads are currently available from Akebono in their Euro and Performance product lines, in Bosch QuietCast brake pads, Performance Friction Carbon Metallic pads, Wagner ThermoQuest pads and several Raybestos brand brake pads. Check for the copper compliance markings on the package.
Pads that meet the new low copper requirements are certified by the Automotive Manufacturers Equipment Compliance Agency (AMECA). Ratings include "A", "B" and "N" edge codes. Each edge code represents a different level of compliance for various contaminants in the friction material. These include copper (Cu), asbestos, chromium (Cr), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg) and cadmium (Cd). Those that meet the highest rating "N" contain less than 0.50 percent copper and no asbestos, chromium, lead, mercury, cadmium or antimony.
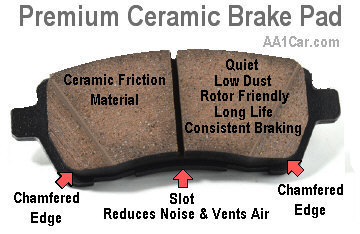
Other features that help make ceramic pads extra quiet include chamfers, slots and insulator shims. These features are also found on other types of pads, but may not be used on all applications.
Chamfers are angled or beveled edges on the leading and trailing ends of the pad that reduce "tip-in" noise when the brakes are first applied. Chamfers also reduce the surface area of the brakes slightly, which increases the clamping force applied by the pads against the rotors. This further helps to dampen sound-producing vibrations.
Slots are grooves cut vertically, diagonally, or horizontally in the pads to reduce noise by changing the frequency of vibration from an audible level to a higher, inaudible frequency beyond the range of the human ear. Slots also help reduce brake fade by providing a passage for gases and dust to escape at high brake temperatures.
Insulator shims provide a dampening layer to absorb and dissipate vibrations before they can cause noise.

Another features of ceramic pads is less visible brake dust on the wheels. All brake pads produce dust as they wear. But the ingredients in ceramic pads typically produce a light colored dust that is much less noticeable, and it does not stick to wheels like ordinary brake dust. Consequently, alloy wheels stay cleaner longer.
Ceramic pads also extend brake life compared to most conventional lining materials. Akebono and Raybestos both say their durability testing has shown significantly longer life with no sacrifice in noise control, rotor life or braking performance when ceramic pads are used compared to other friction materials.
A majority of late model domestic and import vehicles now come factory-equipped with some type of ceramic brake pads. Aftermarket ceramic pads can be installed on any vehicle that is originally-equipped with OEM ceramic pads, or on vehicles that are equipped with Nonasbestos Organic (NAO) linings. Always follow the brake supplier's application recommendations because ceramic brake pads are generally NOT recommended to replace semi-metallic pads, especially on larger, heavier vehicles. On trucks and large SUVs, semi-metallic linings are typically needed to handle higher loads and braking temperatures.
Some aftermarket brake suppliers have also introduced "hybrid" brake pads that combine a ceramic outer brake pad with a semi-metallic or low-metallic compound inner brake pad. They say this combination provides the best of both worlds: the low dusting and quiet braking of the outer ceramic pads with the heat resistance and more aggressive braking of the inner semi-metallic or low-metallic pads.
|
WARNING: DO NOT USE OIL, GREASE, ANTI-SEIZE OR LUBRICANTS OF ANY KIND WHEN TIGHTENING LUG NUTS! Proper torque on lug nuts is very important for three reasons. One is to keep the lug nuts from loosening up and the wheel coming loose, another is to prevent distortion of the brake rotor behind the wheel, and a third is to prevent broken studs. A torque wrench should be used for final tightening of the lug nuts, and the nuts should always be torqued to the recommended specifications. CAUTION: Torque specifications for lug nuts are always for CLEANand DRY studs and lug nuts. That means no oil, no grease, no anti-seize and no lubricants of any kind. Any of these products will reduce the friction between the threads. This may seem like a good thing to prevent rust and frozen lug nuts, but the reduction in friction means a much higher percentage of the applied torque (up to 25% or more) will go toward loading the lug nuts. The end result may be brake rotor distortion or broken studs! Wheel studs should be cleaned with a wire brush to remove rust and dirt BEFORE the wheels are mounted. If the lug nuts are heavily rusted or have damaged threads and won't turn easily on the studs, replace the lug nuts. The same goes for any wheel studs with damaged or badly corroded threads. And remember to mount the wheels DRY with nothing on the threads. |

 More Brake Articles:
More Brake Articles: Click Here to See More Carley Automotive Technical Articles
Click Here to See More Carley Automotive Technical Articles
